| Executive Summary
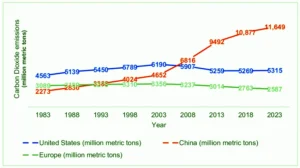
RufusAI offers transformative solutions to significantly reduce the carbon footprint and power consumption of data centers. Leveraging cutting-edge technology, we deliver up to a 40% reduction in energy use, ensuring substantial cost savings and a marked positive impact on the environment. Data Centers and Environmental Impact: According to Cloudscene, there are 299 data centers in the Netherlands as of October 27, 2023. Many of these colocation facilities are in and around Amsterdam. The Netherlands is a popular location for data centers due to its favorable climate, political stability, and well-developed infrastructure. It is also home to the Amsterdam Internet Exchange (AMS-IX), one of the largest internet exchanges in the world. The Dutch data center market is growing rapidly, and new facilities are being built all the time. This growth is being driven by the increasing demand for cloud computing, big data, and other data-intensive applications. As of October 27, 2023, there are approximately 8,000 data center locations worldwide. This number is constantly growing, as the demand for data storage and processing continues to increase. The United States has the most data centers, with over 5,300. Other countries with large numbers of data centers include Germany, the United Kingdom, China, and Japan. Data centers are essential to the modern world, as they power everything from our favorite websites and social media platforms to our cloud-based productivity tools and business applications. They also play a vital role in supporting scientific research and other critical infrastructure. The Dutch Data Center Association (DDA) has set a goal of making the Dutch data center sector climate-neutral by 2030. The DDA is working with its members to develop and implement best practices for reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. 330 million metric tons of carbon dioxide (CO2) equivalent per year. Most of the carbon footprint of data centers comes from the electricity they consume. In 2020, data centers consumed around 3% of the global electricity supply. This is a significant amount of energy, and it is growing rapidly as the demand for data storage and computing power increases. The source of the electricity that data centers consume also plays a role in their carbon footprint. Data centers that are powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, have a smaller carbon footprint than those that are powered by fossil fuels. The efficiency of the servers and cooling systems in a data center can also have a significant impact on its carbon footprint. More efficient servers and cooling systems consume less electricity, which reduces greenhouse gas emissions. The lifetime of the equipment in a data center also plays a role in its carbon footprint. Equipment that is replaced frequently has a larger carbon footprint than equipment that is used for a longer period of time.
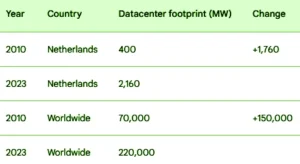
Here are some of the key trends that can be observed from the graph: * The carbon footprint of Dutch data centers has increased from 1.5 million tons of CO2 equivalent in 2013 to 2.5 million tons of CO2 equivalent in 2023. * The growth in the carbon footprint of Dutch data centers has been accelerating in recent years. For example, the carbon footprint of Dutch data centers increased by 10% in 2022, but it is expected to increase by 15% in 2023. * The carbon footprint of Dutch data centers is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, as the demand for cloud computing services continues to increase. However, the growth rate is expected to slow down as the Dutch data center industry takes steps to reduce its carbon footprint. It is important to note that the carbon footprint of Dutch data centers is relatively small compared to the carbon footprint of other industries, such as the energy industry and the transportation industry. However, the carbon footprint of Dutch data centers is growing rapidly, and it is important to take steps to reduce it.
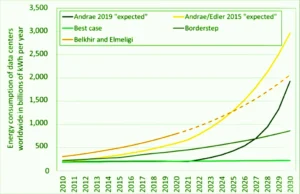
The graph shows that the carbon footprint of data centers worldwide has increased from 200 million tons of CO2 equivalent in 2013 to 330 million tons of CO2 equivalent in 2023. This is an increase of 65% over the past 10 years. The growth in the carbon footprint of data centers is due to a number of factors, including the increasing number of data centers, the growing size and power consumption of data centers, and the increasing use of cloud computing services. The carbon footprint of data centers is a significant contributor to global climate change. Datacenters account for around 3% of global electricity consumption and 2% of total greenhouse gas emissions.
RufusAI lowers the carbon footprint and power consumption by an estimated 40% at the same time it lowers your IT cost. Adjustment every 1 sec without a load on your systems. The system has been tested at one of the largest airports in the USA. RufusAI offers a solution to help companies reduce their carbon footprint by 20-40%, depending on the size and use of their cloud environment. This can lead to lower cloud and energy costs, and a return on investment (ROI) can be proven in a two-month proof of value. RufusAI is confident in its solution and charges a low price for the first two months. If they are unable to achieve the agreed-upon goals, the customer will receive a 50% refund. Here are some of the benefits of using RufusAI: * Reduce your carbon footprint by 20-40% * Lower your cloud and energy costs. * Achieve a positive ROI in two months. * Get a low price for the first two months. * Receive a 50% refund if RufusAI is unable to achieve the agreed-upon goals. If you are interested in learning more about RufusAI and how they can help your company reduce its carbon footprint, please visit their website or contact them for a consultation. -=+ |